If I identify the book by its content, saying “Check out the book called Why Information Grows by César Hidalgo. The ISBN is 0465048994.”, you will be able to get any copy of the book from any source and know that you’re reading the information I recommended.
By contrast, if I used location-addressing to identify the book, I would have to point to a location, saying something like “Go to the news stand at Market & 15th in Philadelphia and ask for the thing 16 inches from the south end of the third shelf on the east wall”
Content-addressed storage or abbreviated CAS, is a way to store information so it can be retrieved based on its content, not its location.
Location-addressed: e.g. HTTP, you lookup a content by its location (URI). Whoever controls the location controls the content. This location-addressed approach forces us all to pretend that the data are in only one location (even if multiple people have copies of it!)
Content-addressed: using the content’s cryptographic hash to identify it. These links are permanent because the cryptographic hash for a piece of content never changes.
See also: CID, block-reference mechanisms
Immutable Objects, Mutable References
The Merkle-DAG, immutable content-addressed objects, and mutable pointers to the Merkle-DAG, instantiate a dichotomy present in many successful distributed systems
IPFS accomplishes this by creating a separate prefix /ipns/<NodeID> ofr mutable paths. One can prove ownership because only the owner of the private key of NodeID can publish to it
Literary Machines
In Ted Nelson’s 1981 Literary Machines, he imagined a universally addressed public repository system
In the computer world this will change, especially if — as I foresee — there will be one great repository and everything will be equally accessible. This means that “different” articles and books will more likely be different versions of the same work, and different pathways through it for different readers
The system promotes the coexistence and resolution of many viewpoints, through the sharing of private documents and comments, and the publication of hypertext complexes whose interrelationships remain orderly.
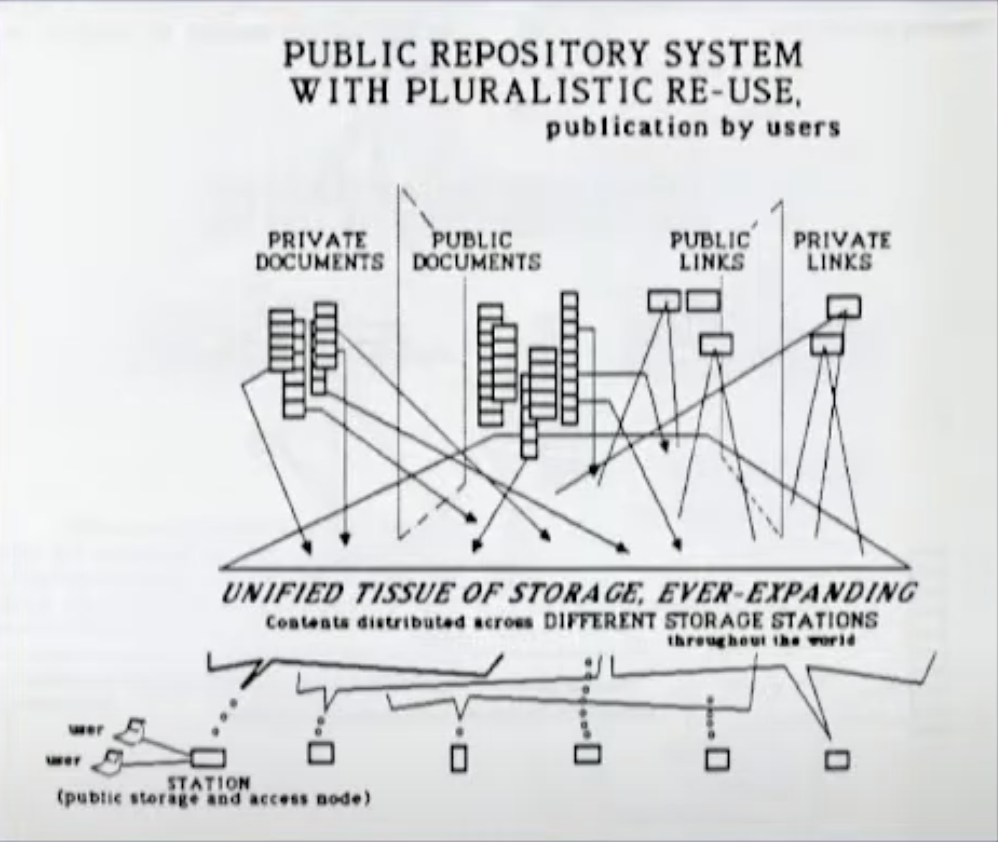
See also: plurality